27 January 2025
Latest index value and inflation rates for Q4 2024
The Statistics Office has released new estimates of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the annual inflation rate. For the fourth quarter of 2024 the CPI has been measured at 103.1; in Q4 2023 the CPI was 95.3, which results in an annual inflation rate of 8.2%. This is much higher than the annual rate for Q3 2024 (which was 2.9%), and is the highest annual rate since 2009.
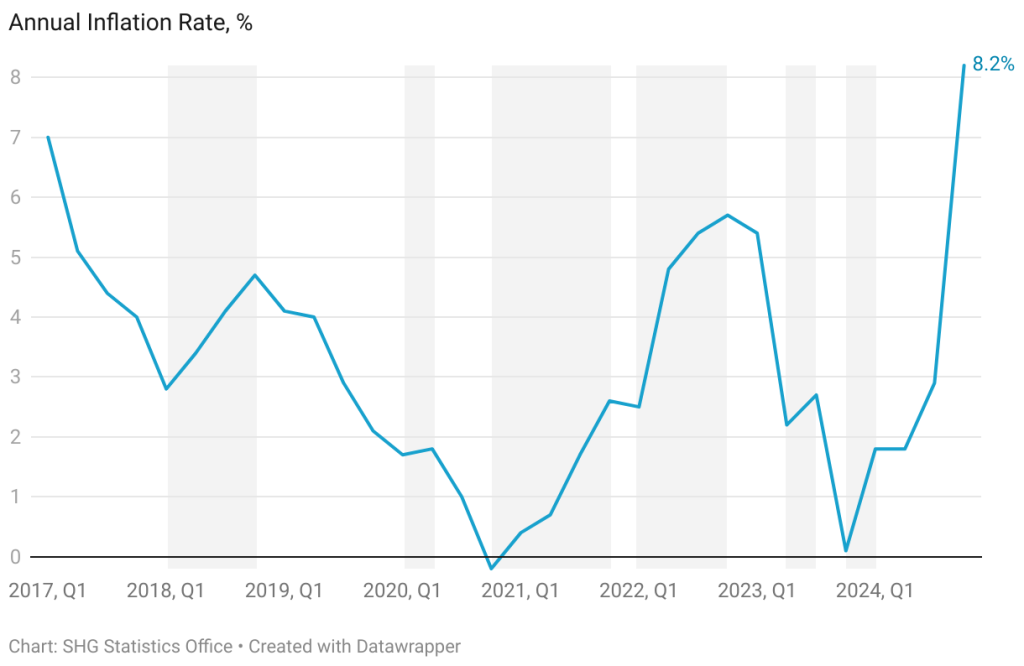
Note that the index has been ‘rebased’ to 100 in Q3, 2024, and there has been a terminology change to Consumer Price Index (from the previous term Retail Price Index) as a result of a slight change in the index composition to make it more internationally consistent.
Price changes over the last year
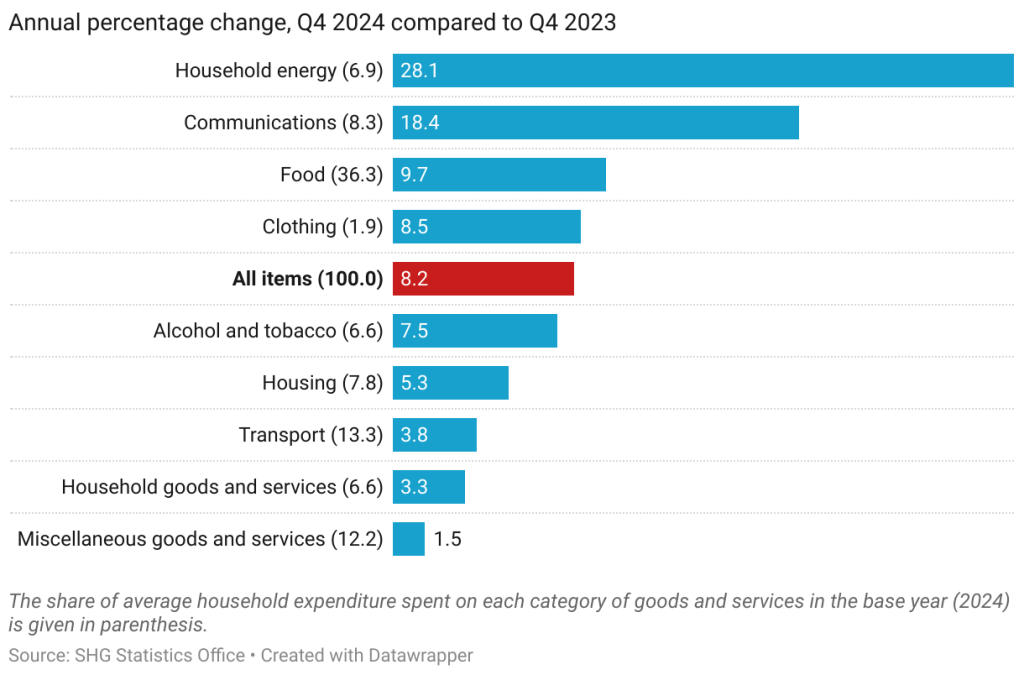
On average, all broad groups of items saw their prices rise compared to a year ago. Some of the most significant changes were increases in electricity prices in January and July, increases in the price of telephone tariff and mobile data packages in July, and increases in the price of bread, local meat, and public transport in December. Additionally, the substantial drop in the price of broadband internet and mobile phone data packages in October 2023 is now no longer affecting the annual price inflation rate. This has resulted in an annual average price increases of 28.1% in Household Energy, 18.4% in Communications, and 9.7% in Food – the annual increase in average Food prices is the highest since Q2, 2017.
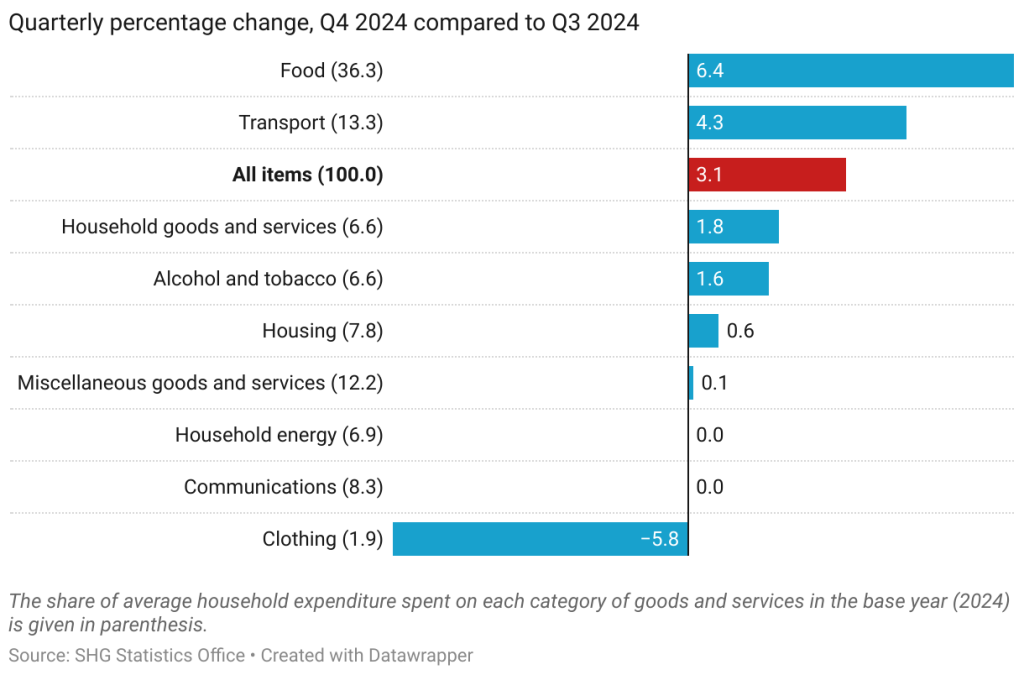
Price changes over the last quarter
The quarterly change in the CPI was 3.1%, comparing Q4 2024 to Q3 2024. All groups of categories experienced average increases since the last quarter, apart from the Clothing, Communications, and Household Energy groups (due to their nature, clothing items tend to change frequently, depending on stock and demand). The groups with the highest quarterly increases were Food (6.4%) and Transport (4.3%), the consequence of an increase in the prices of goods and services, especially bread, meat, and the public bus service.
Note that normally price changes in both the UK and South Africa have a strong impact on prices on St Helena, since the majority of goods imported are purchased in those two countries, although for the Q4 2024 Index, price increases in local goods and services have had a major effect. In December 2024, annual consumer price inflation in the UK was measured at 2.5% (UK Office for National Statistics), down from 2.6% in November. In South Africa, annual consumer price inflation was measured at 3.0% in December 2024 (Statistics South Africa), up from 2.9% in November 2024. Changes in the value of the Rand compared to the Pound can have a large effect on the price of goods purchased in South Africa. For example, for the period January to December 2024, the Pound averaged 23.4 Rand, which is a 2.1% increase compared to the same period in 2023, when it was 23.0. This change tends to counteract the effect of price inflation in South Africa on final shop-floor prices on St Helena.
Methodology
Rebasing the Index
The Index was rebased in the third quarter of 2024, following the 2023 Household Expenditure Survey (HES) and subsequent analysis by the Statistics Office. The HES reviewed the composition of the average ‘shopping basket’ of goods and services purchased by households on St Helena, to make sure it reflects current spending habits. The Statistics Office has also reviewed the items that are used to represent each category of spending in the basket, to make sure they are also up to date and relevant. The rebased Index includes 205 categories of expenditure, within nine broader groupings; these broader groupings are unchanged from the previous Index. Within the broad groupings, the detailed categories of expenditure have been adjusted slightly to better align with international guidelines, and in particular they now only include expenditure related to household consumption, and not all expenditures. This has also made a change to the terminology necessary: the Index has been renamed the Consumer Price Index (CPI), rather than the Retail Price Index (RPI).
What is price inflation and how is it measured?
Price inflation is the change in the average prices of goods and services over time. The rate of price inflation is calculated from the change in the CPI, which is the official measure of the average change in the prices of goods and services paid by consumers. The CPI is estimated each quarter, i.e. once every three months, and the rate of price inflation is usually quoted on an annual basis; that is, comparing price changes over a 12-month period. Prices and the CPI tend to go up, but they can occasionally go down – which is known as price deflation.
The CPI is a statistical measure of the change in consumer prices on St Helena; an increase in the CPI means that, on average, prices have gone up since the last time they were measured, and a decrease in the CPI means that, on average, prices have fallen. The annual change in the CPI is called the annual inflation rate, and is the usual measure of the change in prices in an economy. The CPI is an average measure: if it goes up, it does not mean that all prices have gone up, and similarly, if it goes down, it does not mean that all prices have fallen.
Why do we measure inflation?
An accurate measure of price inflation helps understand the extent and nature of the impact of price changes on the government, businesses, households and individuals. Inflation rates are often used in budgeting and accounting processes so that costs can be adjusted for the effect of price changes.
How is the CPI calculated?
The basis for the CPI is the average weekly cost of goods and services purchased by households on St Helena for consumption, sometimes called the CPI ‘shopping basket’. Items which households purchase more of, such as food, have the biggest share of the CPI basket. The current CPI uses a basket from the latest Household Expenditure Survey in 2023; prices representing the groups of items in the basket are collected every quarter, and the price of the total basket is compared to the price in the baseline period, the third quarter of 2024. By convention, the value of the basket in the baseline period is scaled to 100, and the CPI values are quoted in relation to that baseline. For example, a CPI value of 120 means that average prices have increased by 20 per cent compared to those recorded in the baseline period.
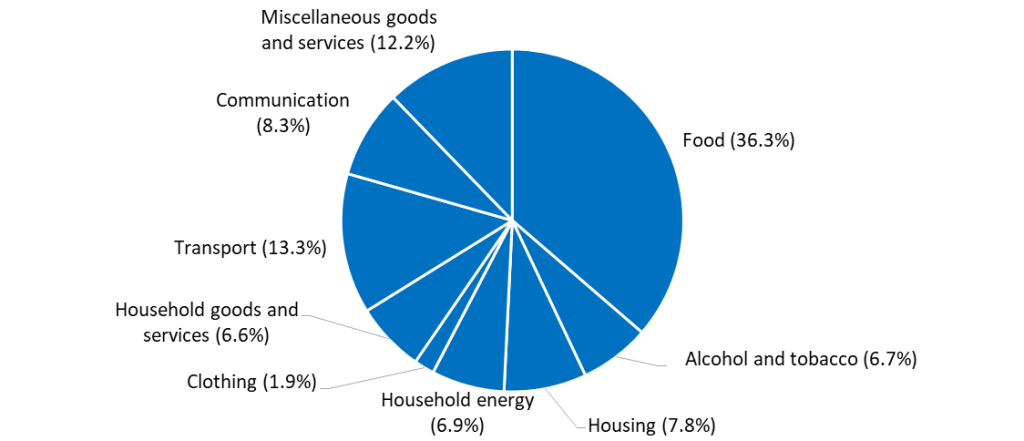
Composition of average household weekly expenditure (Q3 2024 CPI ‘Shopping Basket’)
What happens when items are not available?
If an item of the ‘basket’ is not available then either the previous price will be carried forward from the previous quarter, or a suitable substitute item will be identified and an adjustment calculation made. Care is taken to ensure that this substitute item represents the item category and that it does not introduce error to the measurement of the CPI. An important principle is that price changes should reflect actual price increases and decreases, and not changes in the quality of items.
Where can I get the data?
For detailed tables of the CPI and annual inflation rates from 1994 onwards, please visit: https://www.sainthelena.gov.sh/st-helena/statistics/the-economy and download the ‘inflation’ data file. Other datasets, bulletins and reports are also available on our website: www.sainthelena.gov.sh/statistics.
Have more questions or comments?
Please get in touch. We are Neil Fantom, Statistical Commissioner, Kelly Clingham and Justine Joshua, Senior Statistical Assistants and Courtney O’Dean, Statistics Assistant. You can find us in person at the Statistics Office on the top floor of the Post Office, Jamestown. You can also contact us by telephone on our direct line through 22138. If calling from overseas, the international dialling code for St Helena is +290. Our general office e-mail address is statistics@sainthelena.gov.sh, or you can email team members directly (the format is firstname.lastname@sainthelena.gov.sh).